- Home
- IVD
- By Technology Types
- By Diseases Types
- By Product Types
- Research
- Resource
- Distributors
- Company
This kit enables simultaneous detection of deletions and 11 point mutations in the SMN1 gene, deletions or duplications among any one of the 79 exons and 13 point mutations in the DMD gene, and CGG repeats (premutations or full mutations) in the FMR1 gene. It also provides information of SMN2 gene copy number. It is designed primarily for carrier screening of genetic mutations associated with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and fragile X syndrome (FXS).
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) represents the most common X-linked recessive neuromuscular disease, affecting approximately 1 in 3,500 live male births, with little geographical or ethnic differences. A substantial proportion of affected individuals exhibit familial aggregation; however, about one-third of cases arise from de novo mutations. The primary cause of DMD is a mutation in the DMD gene, with deletions being the most frequent form, accounting for 55%-65% of all cases, predominantly involving exons 44-55 and 2-19. Duplications contribute to 5%-15% of cases, whereas point mutations account for around 30%.
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive neuromuscular disease characterized by degeneration of anterior horn cells of the spinal cord that leads to muscle weakness and atrophy. The incidence is approximately 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 live births, and carrier frequencies are estimated at 1 in 40 to 1 in 50, making it the second cause among childhood fatal autosomal recessive disorders. The 90-95% of individuals affected by SMA is caused by homozygous deletion of the survival motor neuron 1(SMN1) gene; the remaining 3-5% results from compound heterozygous deletion / point mutation (or partial deletion) in the SMN1 gene. The survival motor neuron 2 (SMN2) gene produces 10-20% of full-length functional transcripts. A higher number of SMN2 copies closely correlates with milder clinical phenotype in SMA patients.
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is the most common X-linked recessive monogenic intellectual disability syndrome, accounting for 15%–25% of all X-linked intellectual disability disorders, with its prevalence after trisomy 21 (Down syndrome). Over 99% of FXS cases are caused by expansion and hypermethylation of the CGG trinucleotide repeat sequence (CGG)n in the FMR1 gene. Full mutations (n>200) occur predominantly in males, with an incidence of 1 in 4,000–6,000 males and 1 in 8,000 females. Males and some of females affected with full mutations suffer from severe intellectual disability and self-care deficit, which is incurable and a heavy familial and social burden. Premutations (n=55–200) of the FMR1 gene are associated with diminished ovarian reserve, recurrent miscarriage, premature ovarian insufficiency, infertility, and IVF failure in females, as well as tremor/ataxia syndrome in males during adulthood. The 55x CGG repeat is a dividing line. Individuals with repeat size less than 55 typically have normal phenotypes and low risk of passing on mutations to offsprings. Individuals with repeat size greater than 55 are premutation / full mutation carriers or patients, and more likely transmit a larger repeat size including a full mutation to offsprings, thereby producing more severe clinical phenotypes.
The three genetic conditions above have high incidences, mortality rates and disability rates. No curative treatments are available and medical costs are expensive. However, these conditions can be mitigated by genetic screening for couples who are planning a pregnancy or are pregnant to prevent most of the birth of a child affected by a specific one. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has issued an expert consensus on "Carrier Screening in the Age of Genomic Medicine" that strongly recommends screening for fragile X syndrome and spinal muscular atrophy for all couples who are planning a pregnancy or are pregnant.
Product Name: Human SMN1/DMD/FMR1 mutation detection kit
Certification: FDA
Package Specification: 50 Tests/Kit
Sample Type:
| Applicable PCR Instruments | ABI MiniAmp, ABI VeritiTM Dx, Dongsheng ETC821M, etc. |
| Applicable Genetic Analyzer | ABI 3500 series, ABI 3730 series, Superyears Classic 116, etc. |
| Sample Types | Peripheral blood (at least 1ml), oral swabs (at least 2 counts) |
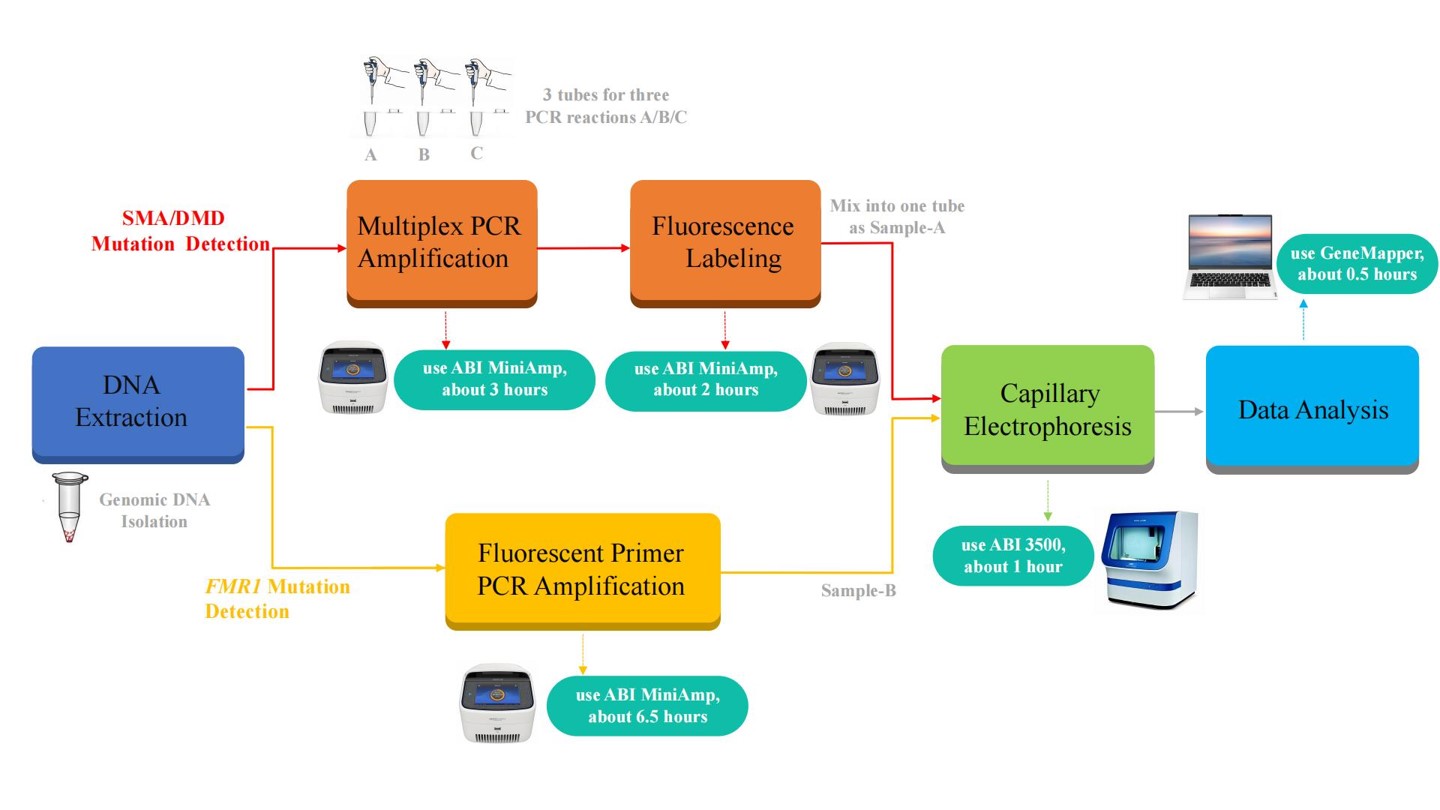
| Testing Time | DNA-to-data in less than 8 hours with easy operation. |
| Result Analysis* | Provides SMN1 and SMN2 gene copy numbers and 11 point mutations, DMD gene copy numbers for any one of all 79 exons and 13 point mutations, and FMR1 gene CGG repeats(capable to detect >200x) |
| Applicable | This product is currently for research use only and cannot be used for clinical diagnosis |
| Cat.No | Product Name | Price |
|---|---|---|
| KP-HYW-0001 | Human SMN1/DMD/FMR1 Mutation Detection Kit | Add To Cart |
|
There is no product in your cart. |